Parameter Mapping
Parameter Mapping allows you to manipulate, transform, and shape data before using it as an input in a node.
Instead of passing raw values directly, you can apply logic, helper functions, and custom expressions to produce exactly the data format you need.
This is especially useful when working with APIs, text formatting, conditional logic, or complex data structures.
Opening the Parameter Mapping Editor
To start parameter mapping:
- Right-click on the node you want to configure
- Select Visual Mapping from the context menu
- The Parameter Mapping Editor opens
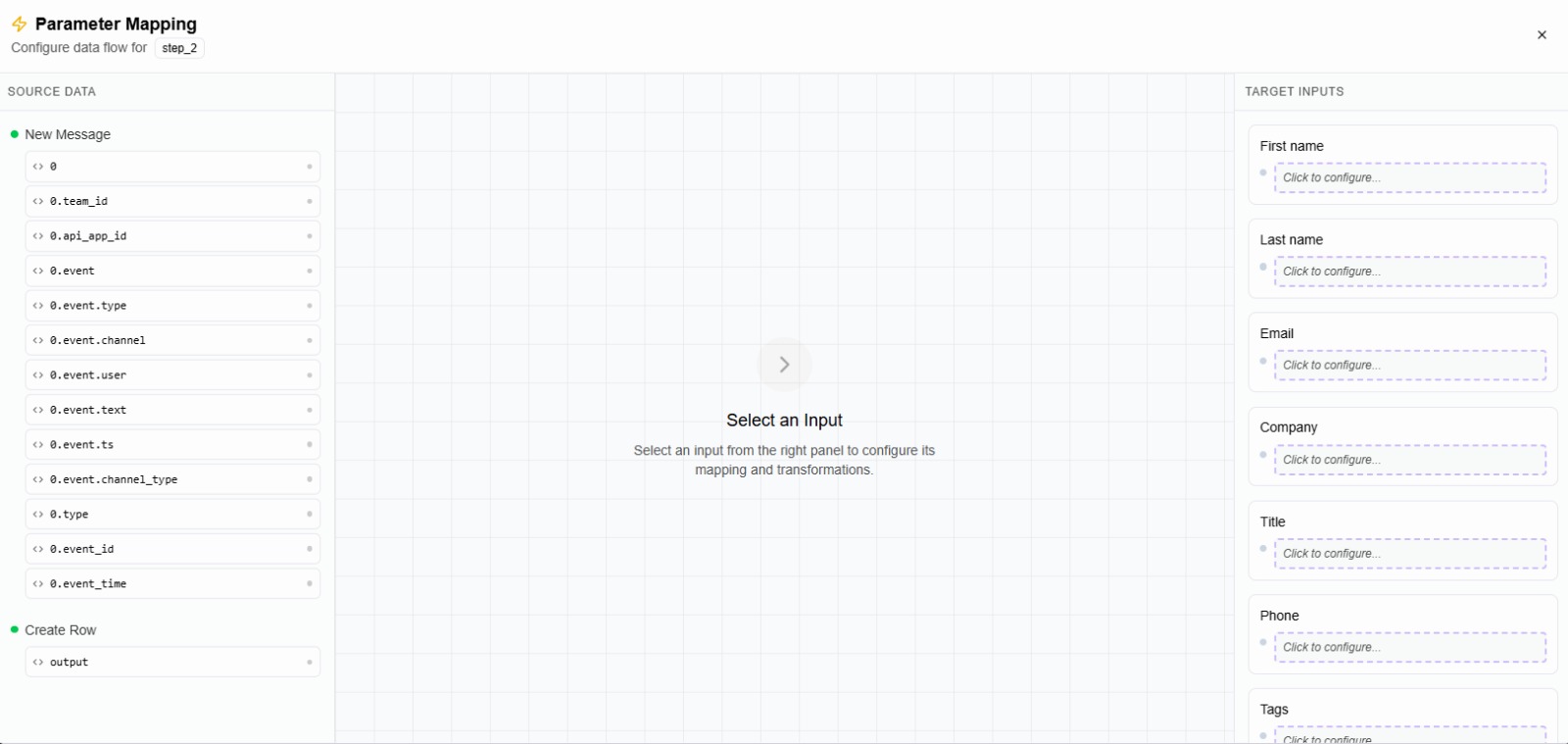
Parameter Mapping Layout
The editor is divided into three main sections:
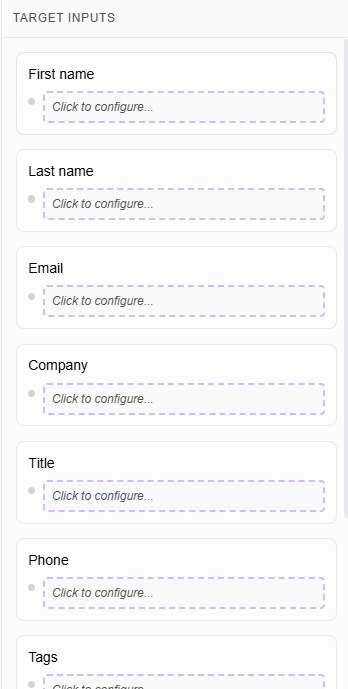
🔹 Right Panel — Target Inputs
This panel shows all configurable input fields of the current node.
- Each input represents a value you can manipulate
- Click on an input to start mapping data for it
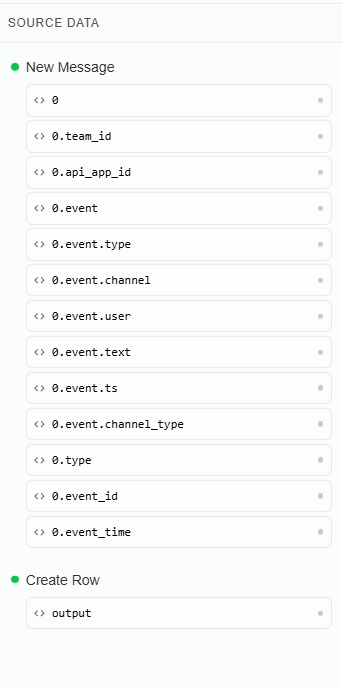
🔹 Left Panel — Source Data
The left side displays all available execution data, including:
- Trigger data
- Outputs from previous nodes
- Nested objects and arrays
This is the data you can use as a source.
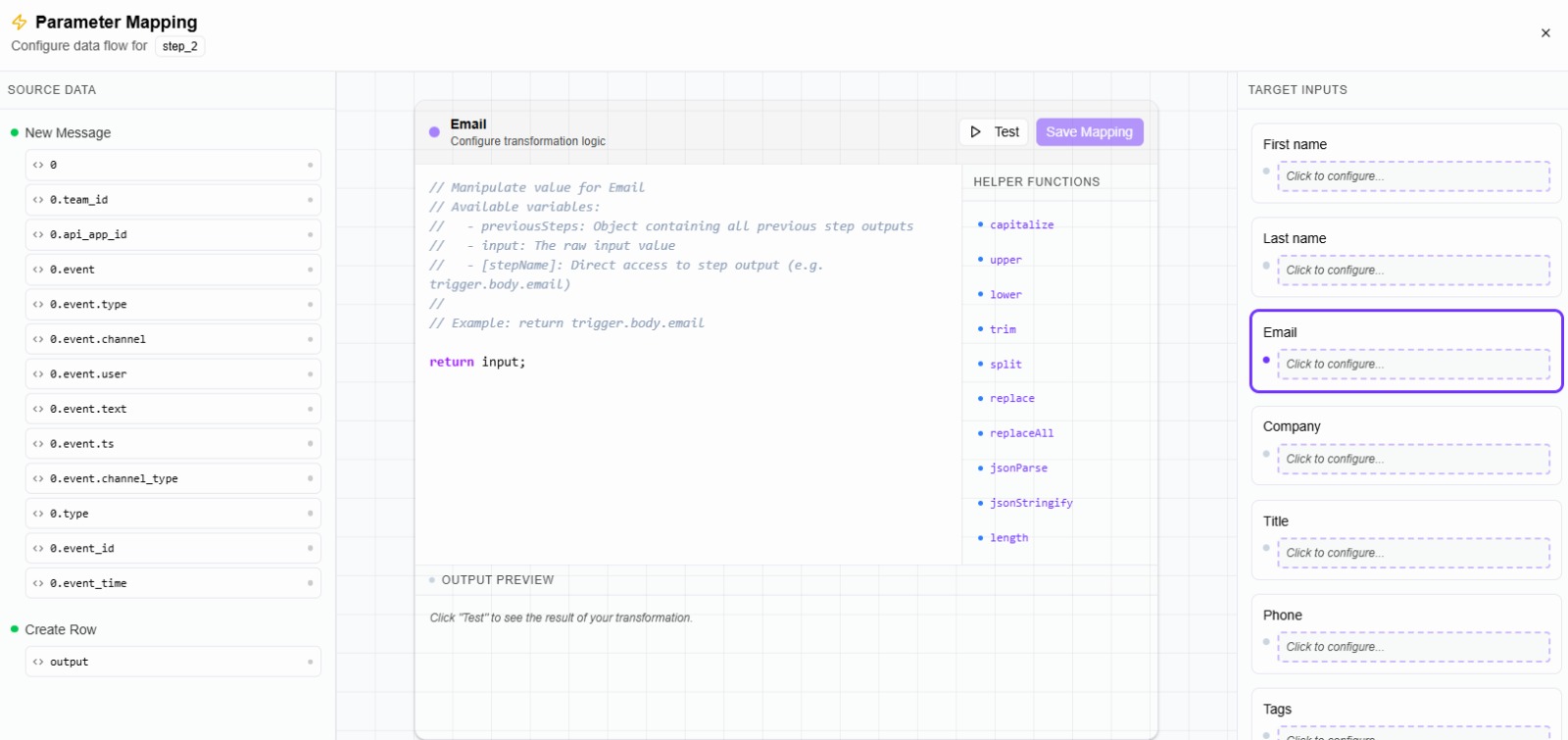
🔹 Center — Code Editor
The center area is the mapping code editor.
Here you:
- Drag source fields into the editor
- Apply helper functions
- Write simple expressions
- Return the final value
The result of this code becomes the value for the selected input.
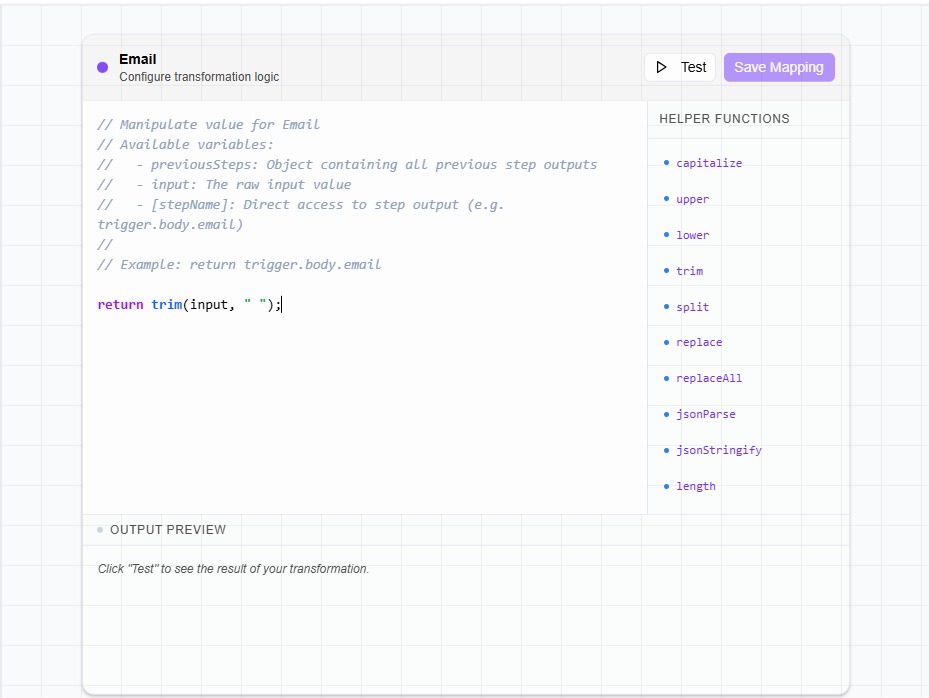
Mapping Data Step by Step
Step 1: Select an Input
Click one of the inputs in the right panel that you want to configure.
Step 2: Drag Source Data
From the left panel, select the data you want to use and drag it into the code editor.
The value is automatically referenced in the mapping code.
Step 3: Apply Helper Functions
On the right side of the editor, you’ll find helper functions.
Helpers are grouped by data type, such as:
- String helpers (uppercase, lowercase, capitalize, trim, replace, etc.)
- Number helpers
- Array helpers
- Date helpers
- Object helpers
You can apply helpers to transform your data as needed.
Step 4: Return the Final Value
At the end of the mapping logic, return the final value.
Only the returned value is used as the input for the node.
Example conceptually:
- Original data → transformed → returned → used as input
return trim(input, " ");
What You Can Do with Parameter Mapping
Parameter Mapping enables you to:
- Format text (uppercase, capitalize, concatenate)
- Extract values from nested objects
- Combine multiple fields into one value
- Prepare API-ready payloads
- Normalize data formats
- Apply simple logic before execution
All transformations happen at runtime, using real execution data.
Important Notes
- Parameter mapping runs during execution
- It does not modify the original source data
- Each execution evaluates mappings independently
- Invalid mappings will surface as execution errors
When to Use Parameter Mapping
Use parameter mapping when:
- Raw data does not match the required input format
- APIs expect specific payload structures
- You need dynamic, computed input values
- You want to avoid extra transformation nodes
Summary
- Open Visual Mapping via right-click on a node
- Select an input to configure
- Drag execution data into the code editor
- Apply helper functions as needed
- Return the final transformed value
Parameter Mapping is the core tool for flexible, dynamic data manipulation in puq.ai workflows.